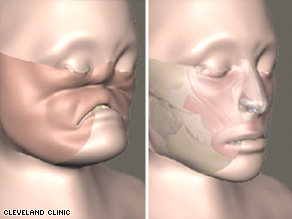
The woman who received the first-ever near-total face transplant in the United States told her doctor she has regained her self-confidence, said Dr. Maria Siemionow, head of plastic surgery research at the Cleveland Clinic and leader of the transplant team.
The patient, who prefers to be anonymous, is finally able to breathe through her nose, smell, eat solid foods and drink out of a cup, Siemionow told participants of the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Chicago over the weekend. The complex surgery, a 22-hour procedure, took place in December at the Cleveland Clinic. The patient received her new face in one graft from a donor cadaver. “I believe this procedure is justified because you need a face to face the world,” Siemionow said. Watch an animation of the face transplant » The patient had previously “suffered severe facial trauma,” the Cleveland Clinic said. She had no nose, right eye or upper jaw before the procedure, and could not smell or eat normally. People would call her names on the street, Siemionow said. The surgery gave the patient a nose with nasal lining, as well as a palate. This, combined with the olfactory receptors in the brain, gave the patient the ability to smell, Siemionow said. Social reincorporation is as important as the face transplant itself, Siemionow said. At this point, the patient doesn’t want to face the “common world,” but she is facing her family, the surgeon said.
Don’t Miss
Surgery transplanted most of patient’s face
The patient said she is happy because when she puts her hands on her face, she feels a nose, Siemionow said. She can also taste a hamburger and pizza, and drink coffee from a cup, the “things we take for granted every day,” Siemionow said. The patient also received lower eyelids, upper lip, skin, muscles, bone, hard palate, arteries, veins and nerves. As for the aesthetics of the new face, Siemionow suggested that restoring function was more important. “At this point, no one is really looking at beautification,” she said. Siemionow, who has been working on face transplant research for 20 years, received approval from the Institutional Review Board in 2004 to conduct a full facial transplant. Only patients who had already exhausted all possible options for conventional repair were considered for the transplant, Siemionow said. Currently, cancer patients are not candidates for face transplants because transplant recipients must take immunosuppression drugs for life so that the body does not reject the donated tissue, Siemionow said. In the future, however, lifelong immunosuppression may not be required, she said. While burn damage is normally patched with pieces of excess skin from a person’s own body, this does not work if the whole face needs to be covered — the skin of the entire back is less than half of what would be needed to cover the full face and scalp, Siemionow said. Previously, three facial transplants had been completed — two in France and one in China. The Chinese recipient, Li Guoxing, died in July of unknown causes, Guo Shuzhong, a doctor involved in the case, confirmed to CNN. One of the French face transplant recipients was a man who had a genetic disorder that created large tumors on his face. The other French patient had been bitten by a dog. The Chinese patient had been attacked by a bear. European news media recently reported that a surgeon in Spain received approval for another face transplant, which would be the fifth in the world. Researchers are also making headway into treatments for disorders that give rise to facial abnormalities, experts say. They are identifying genes that become mutated and cause the skull and facial features to become distorted.
Health Library
MayoClinic.com: Cosmetic surgery
“We’re moving into the arena where we can do medical treatment,” Dr. Ethylin Jabs, professor of developmental and regenerative biology at Mount Sinai Medical School, said at the conference. One example is Treacher Collins syndrome, a condition found in one in every 50,000 births, which affects the development of bones and other tissues in the face. Scientists have determined that the gene TCOF1 is involved in the disorder, and research is ongoing into the precise function of this protein.
By looking at the genetic underpinnings of disorders that lead to facial deformities, scientists can also understand what accounts for the normal differences in face and skull types. “These are going to be some of the genes that cause some of that variation,” Jabs said.